Data Architecture
Data Architecture
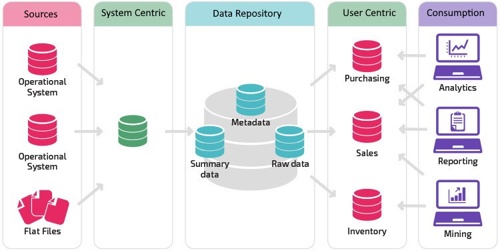
Data architecture is a framework for how IT infrastructure supports your data strategy. The goal of any data architecture is to show the company's infrastructure how data is acquired, transported, stored, queried, and secured. A data architecture is the foundation of any data strategy.
Some of the foundations of modern data architecture are:
- Data is a shared asset - A modern data architecture needs to eliminate departmental data silos and give all stakeholders a complete view of the company.
- Users require adequate access to data - Beyond breaking down silos, modern data architectures need to provide interfaces that make it easy for users to consume data using tools fit for their jobs.
- Security is essential - Modern data architectures must be designed for security and they must support data policies and access controls directly on the raw data.
- Common vocabularies ensure common understanding - Shared data assets, such as product catalogs, fiscal calendar dimensions, and KPI definitions, require a common vocabulary to help avoid disputes during analysis.
- Data should be curated - Invest in core functions that perform data curation (modeling important relationships, cleansing raw data, and curating key dimensions and measures).
- Data flows should be optimized for agility - Reduce the number of times data must be moved to reduce cost, increase data freshness, and optimize enterprise agility.
Modern data architecture consists of the following components:
- Data pipelines - A data pipeline is the process in which data is collected, moved, and refined. It includes data collection, refinement, storage, analysis, and delivery.
- Cloud storage - Not all data architectures leverage cloud storage, but many modern data architectures use public, private, or hybrid clouds to provide agility.
- Cloud computing - In addition to using cloud for storage, many modern data architectures make use of cloud computing to analyze and manage data.
- API Access - Modern data architectures use APIs to make it easy to expose and share data.
- AI and ML models - AI and ML are used to automate systems for tasks such as data collection, labeling, etc. At the same time, modern data architectures can help organizations unlock the ability to leverage AI and ML at scale.
- Data streaming - Data streaming is flowing data continuously from a source to a destination for processing and analysis in real-time or near real-time.
- Real-time analytics - The goal of many modern data architectures is to deliver real-time analytics, the ability to perform analytics on new data as it arrives in the environment.
Modern data architectures must be designed to take advantage of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), automation, internet of things (IoT), and blockchain. The following are some best practices which you should try and incorporate into the architecture.
- Cloud-native -Modern data architectures should be designed to support elastic scaling, high availability, end-to-end security for data in motion and data at rest, and cost and performance scalability.
- Scalable data pipelines -To take advantage of emerging technologies, data architectures should support real-time data streaming and micro-batch data bursts.
- Seamless data integration - Data architectures should integrate with legacy applications using standard API interfaces. They should also be optimized for sharing data across systems, geographies, and organizations.
- Real-time data enablement - Modern data architectures should support the ability to deploy automated and active data validation, classification, management, and governance.
- Decoupled and extensible - Modern data architectures should be designed to be loosely coupled, enabling services to perform minimal tasks independent of other services.
Data Engineers have experienced certified consultants who are able to help guide you through things
